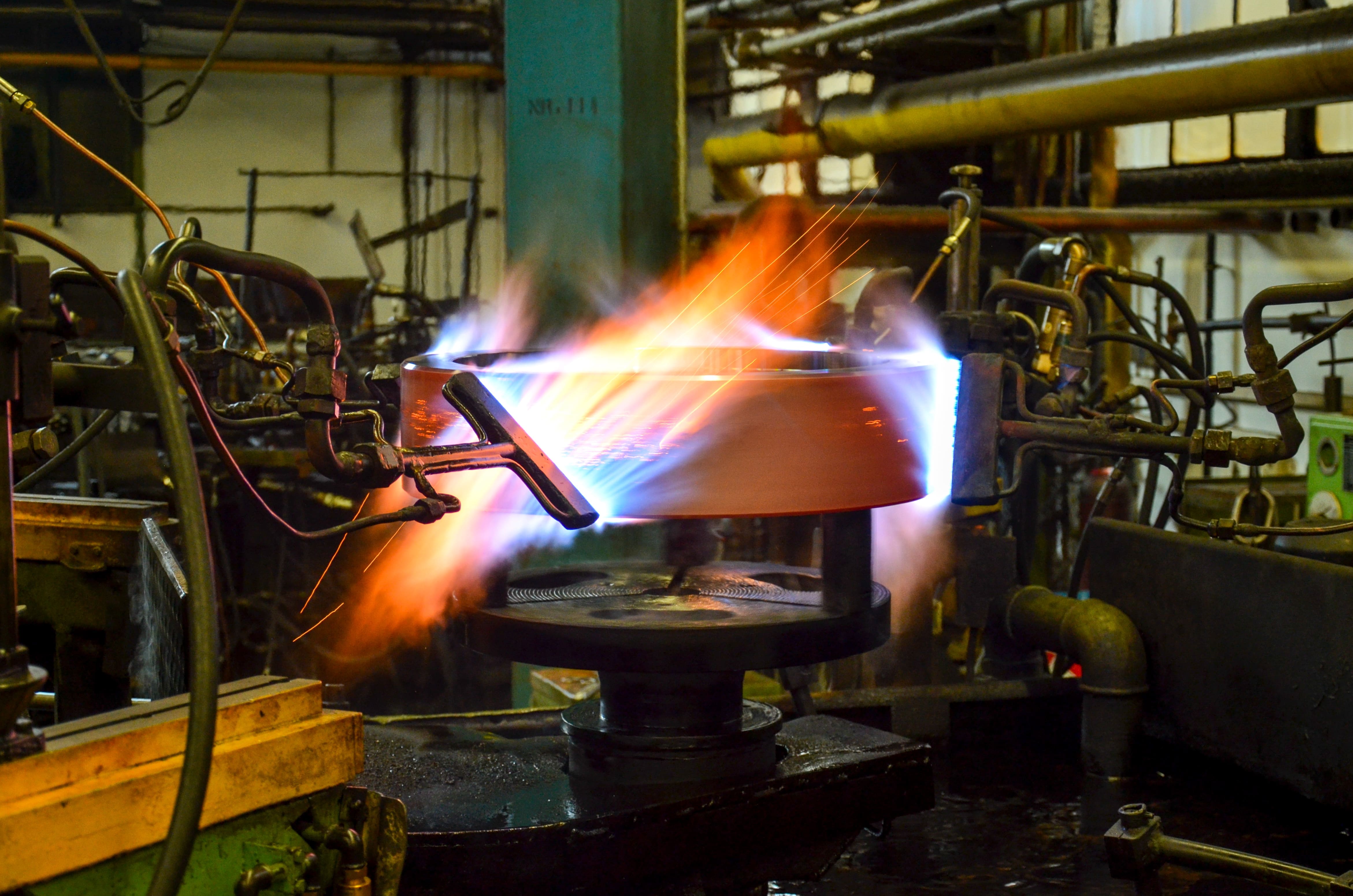
Flame hardening
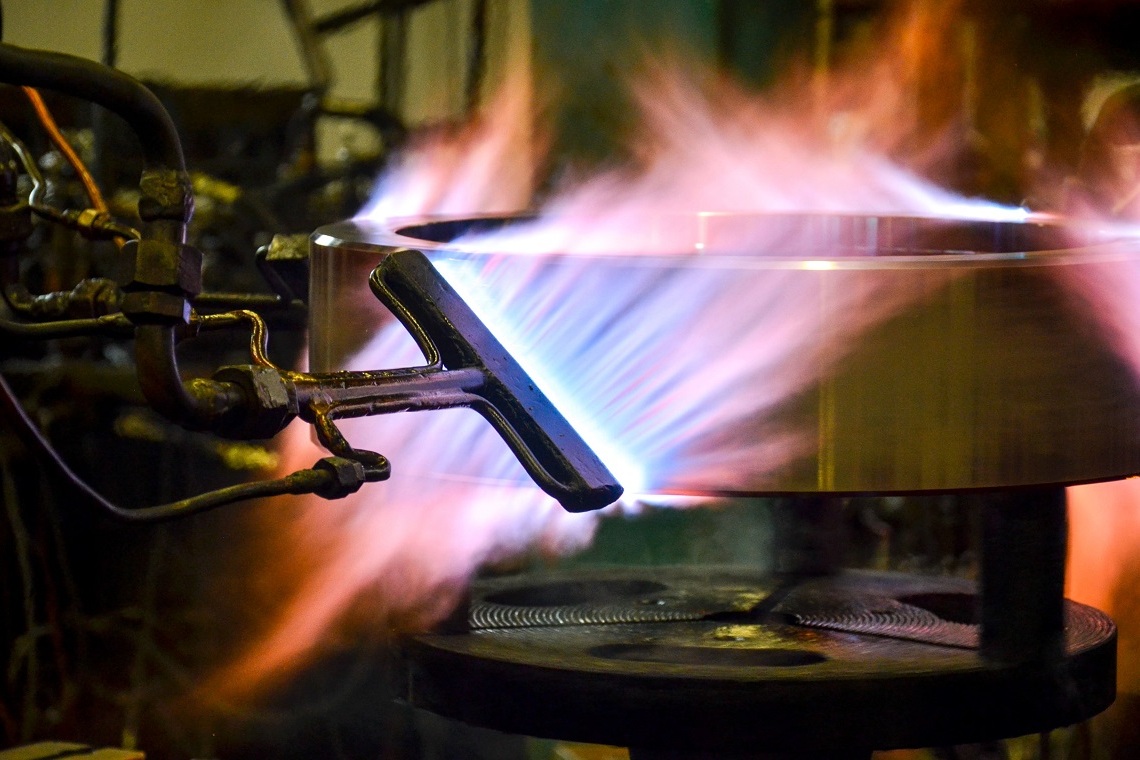
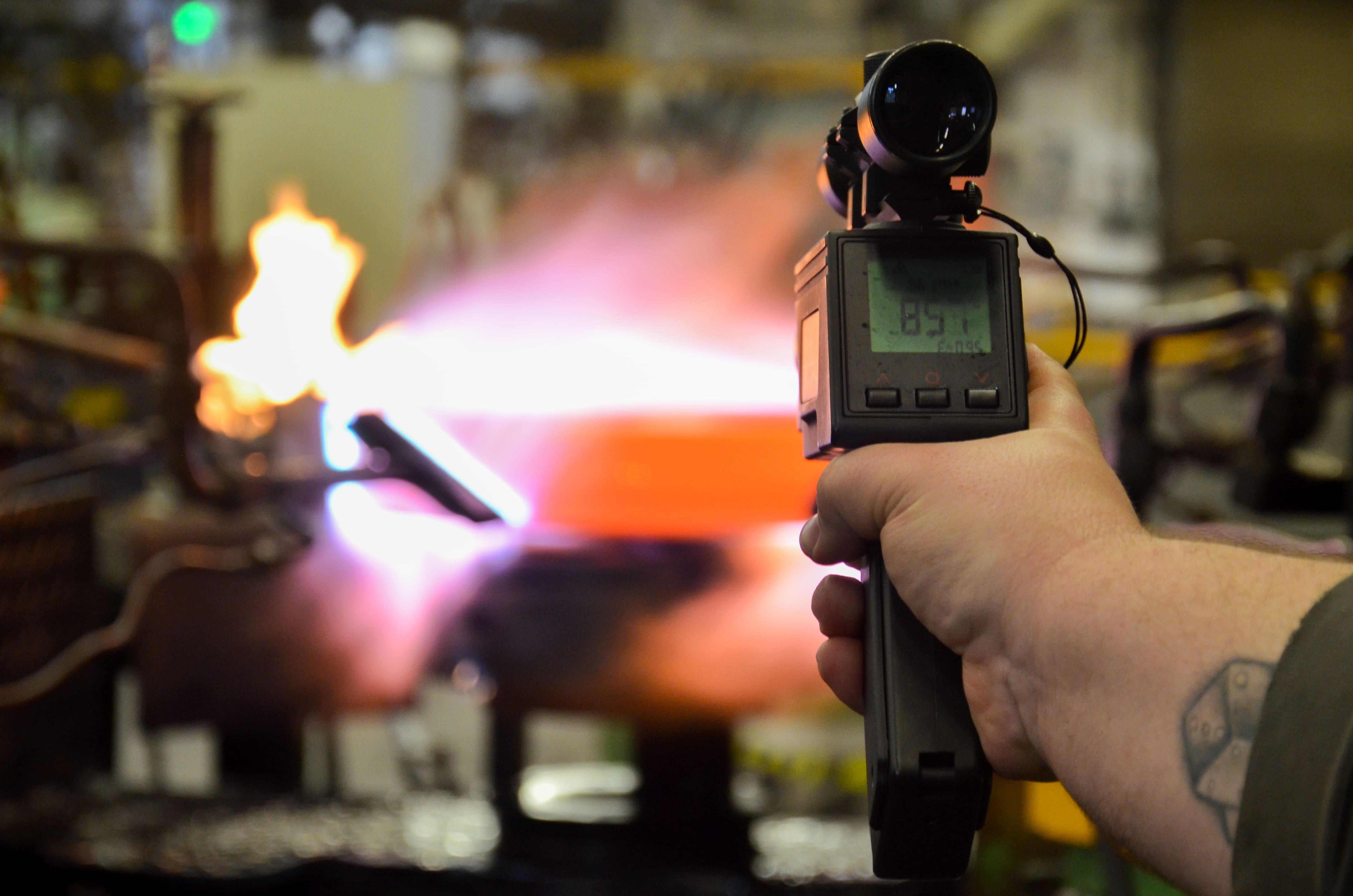
Just like inductive hardening, flame hardening belongs to the case-hardening process group. The aim of this process is to increase the mechanical resilience of precisely defined areas of a component which are subjected to increased stresses in operational use. To this end, the corresponding areas are heated quickly using high-performance burners to reach the hardening temperature (austenitising temperature) and then quenched directly. Depending on the material and desired surface hardness, water, polymer solutions, special hardening oils or compressed air are available as quenching media.
Subsequent tempering both relieves the stresses that have arisen in the part through hardening and, through appropriate temperature selection, sets the desired surface hardness of the component.
Suitable materials
Almost all Q&T steels with a carbon content ˃ 4%, as well as cast and high-alloy materials (with sufficient free carbon content) are suitable for this hardening process. Depending on the material, hardening depths of over 30 mm can be achieved.
Applications
- Spin hardening
- Progressive spin hardening
- Progressive hardening
- Flank and root hardening
- Head hardening
- and the production of part-specific burners, it is possible to process all component shapes.
Advantages of flame-hardening
- Even hardness profile
- Exact hardness of defined areas (hard surface – tough core)
- Minimal distortion
- High reproducibility
- High throughput
- Economical processing
Own burner and inductor manufacturing
At its Gevelsberg site, the Hanomag Lohnhärterei Group as a company can offer over 90 years’ experience in case-hardening.
We build our own burners and inductors. With our mobile hardening equipment, we can also harden large components on site at the customer.